Chapter 7. Origin Server¶
This chapter will explain the relationship between STON and the origin server. The origin server generally refers to the web server that abides by the HTTP standard. For the sake of protecting the origin server, administrators should have a thorough understanding of the contents of this chapter. Doing so will enable you to establish a service that’s flexible and resistant to origin server errors.
The origin server must be protected. With a variety of ways errors can occur, there are a variety of countermeasures to deal with them. Having a proper protection policy for the origin server will make it easier during inspection.
Error Detection and Recovery¶
If an error occurs in the origin server during caching, the server is automatically excluded. When the server is judged to be stable, it will be brought back into the service.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<ConnectTimeout>3</ConnectTimeout>
<ReceiveTimeout>10</ReceiveTimeout>
<Exclusion>3</Exclusion>
<Recovery Cycle="10" Uri="/" ResCode="0" Log="ON">5</Recovery>
<ConnectTimeout> (default: 3 sec)If a connection to the origin server cannot be made within the set amount of time, it will be considered a connection failure.
<ReceiveTimeout> (default: 10 sec)If the origin server does not return an HTTP response for a normal HTTP request within the set amount of time, it will be considered a transaction failure.
<Exclusion> (default: 3 times)If an error occurs (
<ConnectTimeout>or<ReceiveTimeout>) consecutively for the set number of times, the corresponding server will be excluded from the available server list. The value will be reset to 0 if a successful communication occurs before exclusion.<Recovery> (default: 5 times)If the origin server responds with
ResCodewhenUriis requested everyCycleconsecutively for the set number of times, the corresponding server will be restored. If this value is set to zero, the server will not be restored.Cycle (default: 10 sec)Makes a new request after the set amount of seconds.Uri (default: /)The Uri to be sent in the request.ResCode (default: 0)The response code to be identified as normal. If set to 0, any response will be considered a success regardless of the response code. If set to 200, the response code must be 200 for the response to be identified as normal. Commas (,) can be used to set multiple response codes. For example, if set to “200, 206, 404”, then any one of those response codes will be identified as normal.Log (default: ON)Records the HTTP transaction that was used for recovery to the Origin Log.
Health-Checker¶
Error Detection and Recovery responds to errors that occur during the caching process. <Recovery> will terminate an HTTP transaction as soon as a response code is received. However, Health-Checker checks for a successful HTTP transaction.
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost>
<Origin>
<Address> ... </Address>
<HealthChecker ResCode="0" Timeout="10" Cycle="10"
Exclusion="3" Recovery="5" Log="ON">/</HealthChecker>
<HealthChecker ResCode="200, 404" Timeout="3" Cycle="5"
Exclusion="5" Recovery="20" Log="ON">/alive.html</HealthChecker>
</Origin>
<HealthChecker> (default: /)Configures Health-Checker. Multiple configurations are allowed. Uri is used as the input, and CDATA is used for invalid XML characters.
ResCode (default: 0)The correct response code (multiple codes can be assigned with commas).Timeout (default: 10 sec)The available time from the socket connection until the HTTP transaction is completed.Cycle (default: 10 sec)The execution period.Exclusion (default: 3 times)The number of consecutive failures before excluding the server.Recovery (default: 5 times)The number of consecutive successes before reintroducing the server.Log (default: ON)Records the HTTP Transaction to the Origin Log.
Health-Checker can be configured in multiple ways and can be executed independently of client requests. It does not share information with Error Detection and Recovery or other Health-Checkers and uses only its own information to decide exclusion and recovery.
Origin Address Use Policy¶
The following factors are considered in deciding how to use the origin address (IP).
- Origin Server address format (IP or domain) and standby address
- Error Detection and Recovery
- Health-Checker
As a service is run, the origin address being excluded and recovered will occur frequently. STON uses IP Table-based origin addresses and provides information via the Origin Status Monitoring API.
It is simpler to set the origin address with an IP instead of a domain.
- Nothing will be able to change the IP list except for configuration changes.
- The IP address will not expire based on the TTL.
- Exclusion/recovery will work based on the IP address.
If the origin address is set with a domain, it must be resolved in order to obtain the IP. (This will be saved in the DNS Log.) The IP list will be able to be changed dynamically, and IPs will only be valid during the TTL.
- The domain will be resolved periodically (1~10 s).
- The IP Table to be used will be organized based on the resolving results.
- All IPs will be valid during the TTL and will not be used when the TTL expires.
- If an identical IP is resolved, the TTL will be refreshed.
- The IP Table cannot be empty. Even if the TTL is expired, the last IP will never be deleted.
Even if the origin address is set to a domain, error/recovery will work based on the IP address. Here there is something to keep in mind. The DNS client (STON) is unable to know the exact IP list for a domain. If a domain consists of only unavailable IP addresses, then it may constantly be in a state of error.
The domain address error/recovery policy is as follows.
- If all known IP addresses for a domain are excluded (Inactive), then the corresponding domain will also be excluded.
- Even if a new IP is resolved, if the domain is excluded then the IP address will also be excluded.
- Even if the TTLs of all IPs expire, this will not change the state of the excluded domain.
- At least one IP of an excluded domain must be recovered for that domain to also be recovered.
It is recommended to improve your understanding of service behavior through the Origin Status Monitoring API.
Origin Status Monitoring¶
An API is used to monitor the state of a virtual host’s origin server.
http://127.0.0.1:10040/monitoring/origin // All virtual hosts
http://127.0.0.1:10040/monitoring/origin?vhost=www.example.com
The results are given in JSON format.
{
"origin" :
[
{
"VirtualHost" : "example.com",
"Address" :
[
{ "1.1.1.1" : "Active" },
{ "1.1.1.2" : "Active" }
],
"Address2" : [ ],
"ActiveIP" :
[
{ "1.1.1.1" : 0 },
{ "1.1.1.2" : 0 }
] ,
"InactiveIP" : [ ]
},
{
"VirtualHost" : "foobar.com",
"Address" :
[
{ "origin.foobar.com" : "Active" }
],
"Address2" : [ ],
"ActiveIP" :
[
{ "5.5.5.5" : 21 },
{ "5.5.5.6" : 60 },
{ "5.5.5.7" : 37 }
],
"InactiveIP" :
[
{ "5.5.5.8" : 10 },
{ "5.5.5.9" : 184 }
]
}
]
}
VirtualHostThe virtual host name.AddressOrigin Server. It will returnActiveif the address is being used, andInactiveif not being used (due to an error).Address2Standby Origin Server Address. It will returnActiveif the address is being used, andInactiveif not being used.ActiveIPThe list of IPs in use and their TTLs. If the origin server is set with an IP address, an identical IP will be shown inAddresswith a TTL of 0. If set with a domain, the values depend on the resolving results. Various IPs and TTLs are used.InactiveIPThe list of IPs not in use and their TTLs. Even though they are not in use, they can still be in a recovery status or being managed by Health-Checker. If the address is not recovered within the TTL, it will be removed.
Origin Status Reset¶
An API is used to reset the exclusion/recovery of origin servers of a virtual host. The current session will not be reused, and a new connection will be created instead.
http://127.0.0.1:10040/command/resetorigin // All virtual hosts
http://127.0.0.1:10040/command/resetorigin?vhost=www.example.com
Overload Detection¶
Content requested for the first time must always be retrieved from the origin server. However, content already cached can be taken care of more flexibly. If STON detects that the origin server is overloaded, renewal of content can be postponed so as to not increase server load.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<BusySessionCount>100</BusySessionCount>
<BusySessionCount> (default: 100)If the number of HTTP transactions taking place on the origin server exceeds the set value, it will be considered an overload. So that the origin server isn’t further accessed to renew expired content, the TTL is extended by the value of<OriginBusy>in Time To Live (TTL). This value can be set to a very large number if you want all requests to go to the origin server.
Origin Selection¶
This configures the origin server selection policy in the case when the origin server consists of multiple addresses (two or more).
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<BalanceMode>RoundRobin</BalanceMode>
<BalanceMode> (default: RoundRobin)RoundRobin (default)The server will be chosen via round-robin so that all origin servers receive requests uniformly. Connected idle sessions are only used when a request to the corresponding server is necessary.SessionA session will be used if it can be reused. If a new session is necessary, the next server will be chosen via round-robin.HashContent will be requested in a dispersed way following the consistent hashing algorithm. If a server is chosen, the current session will be reused; if there is no session, a new one will be created.
| / | RoundRobin | Session |
|---|---|---|
| Load (Requests) | Load is divided equally across servers | Higher load on servers with better responsiveness and reusability |
| Connection cost | High (Finds a connection or attempts a new one for each server) | Low (Only connects when the session can’t be reused) |
| Reusability | Low (Server division is prioritized) | High (Already-connected sessions are prioritized) |
| Session count | Many (Sum of simultaneous HTTP transactions for each server) | Few (Only as many sessions as there are HTTP transactions) |
Session Recycle¶
If the origin server supports the Keep-Alive setting, then the connected session will always be reused. However, the origin server can unilaterally terminate connections to recycled sessions. As a result, the connection will need to be recovered, which can potentially lower user responsiveness. This is especially the case for sessions that haven’t been used in a while. To prevent this, sessions that aren’t reused for the set number of seconds will have their connection be automatically terminated.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<ReuseTimeout>60</ReuseTimeout>
<ReuseTimeout> (default: 60 s)Terminates sessions that have not been used within the set amount of time. If set to zero, origin server sessions will not be reused.
Range Request¶
Configures how much content is downloaded at a time. If the content is generally viewed from the front, such as videos, then setting a limit to the download size can reduce unnecessary origin traffic.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<PartSize>0</PartSize>
<PartSize> (default: 0 MB)If set to greater than zero, a range request will be used to download the set value (MB) starting from the point requested by the client.
Another reason to use <PartSize> is to save disk space. Under default settings, STON generates a file with the same size as the original on the disk. However, as long as <PartSize> is not zero, the file will be partitioned to the given size and saved.
For example, if a client watches the first minute (10 MB) of a one-hour (600 MB) video, only 10 MB of the disk space will be used. There is some benefit in saving disk space, but because the file is saved in parts, the disk load increases a little.
Note
When content is downloaded for the first time, the content length is unknown and a range request cannot be made. Therefore, if <PartSize> is configured, the connection will be closed after the set size is downloaded.
Initializing the Entire Range¶
Generally, whether a file is downloaded for the first time or is being checked for renewal on the origin server, the same simple GET request is sent.
GET /file.dat HTTP/1.1
However, origin servers configured to always modify files for general GET requests may have issues because the original file cannot be cached in its original form.
One of the most common examples is when the Apache web server embeds external modules such as mod_h.264_streaming. The Apache web server will always respond using the mod_h.264_streaming module. As such, the client (in this case, STON) will not receive the file as it originally was but a file modified by the module.
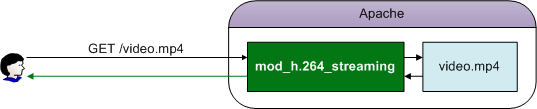
The mod_h.264_streaming module always modifies the original file.
A range request can be used to bypass the module and download the original.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<FullRangeInit>OFF</FullRangeInit>
<FullRangeInit>OFF (default)A normal HTTP request is sent.ONA range request that begins with 0 is sent. In Apache, if the range header is specified, the module is bypassed.GET /file.dat HTTP/1.1 Range: bytes=0-
Because the Range can’t be known when a file is cached for the first time, Full-Range (starting with 0) is requested. You must verify that a normal response (206 OK) is returned for range requests.
If content is being renewed, the If-Modified-Since header will also be specified as below. The origin server must properly respond with 304 Not Modified.
GET /file.dat HTTP/1.1
Range: bytes=0-
If-Modified-Since: Sat, 29 Oct 1994 19:43:31 GMT
Note
The following is a list of web servers where <FullRangeInit> is confirmed to work properly.
- Microsoft-IIS/7.5
- nginx/1.4.2
- lighttpd/1.4.32
- Apache/2.2.22
Keeping Client Requests¶
You can configure whether client requests are kept or changed via the Caching-Key.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<WholeClientRequest>OFF</WholeClientRequest>
<WholeClientRequest>OFF (default)The Caching-Key is used as the URL requested to the origin server.ONThe URL requested by the client is requested to the origin server.
To raise the Hit Ratio, the following settings are used to select the Caching-Key.
Therefore, the URL and Caching-Key requested to the origin server is determined in the following way.
| Setting | Client Requested URL | Origin Requested URL / Caching-Key |
|---|---|---|
Case Sensitivity OFF |
/Image/LOGO.png | /image/logo.png |
Case Sensitivity ON |
/Image/LOGO.png | /Image/LOGO.png |
QueryString Differentiation OFF |
/view/list.php?type=A | /view/list.php |
QueryString Differentiation ON |
/view/list.php?type=A | /view/list.php?type=A |
If <WholeClientRequest> is set to ON, the URL sent by the client will be sent as is to the origin, regardless of the Caching-Key.
| Setting | Client/Origin Requested URL | Caching-Key |
|---|---|---|
Case Sensitivity OFF |
/Image/LOGO.png | /image/logo.png |
Case Sensitivity ON |
/Image/LOGO.png | /Image/LOGO.png |
QueryString Differentiation OFF |
/view/list.php?type=A | /view/list.php |
QueryString Differentiation ON |
/view/list.php?type=A | /view/list.php?type=A |
When POST requests are cached and requested to the origin server, the body data of the POST request sent by the client is transmitted without modification.
Note
Because URLs sent by the client are not modified in anyway, QueryStrings added using functions such as Trimming will also be sent wihout modification.
Origin Request Default Header¶
Host Header¶
Configures the Host header of the HTTP request sent to the origin server. If not specified, the virtual host name will be used.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<Host />
<Host>Configures the Host header sent to the origin server. If the origin server uses a port other than 80, the port must be specified.# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions> # vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions> <Host>www.example2.com:8080</Host>
If you want to send the Host header from the client to the origin, * is used.
User-Agent Header¶
Configures the User-Agent header of the HTTP request sent to the origin server.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<UserAgent>STON</UserAgent>
<UserAgent> (default: STON)Configures the User-Agent header sent to the origin server.
If you want to send the User-Agent header from the client to the origin, * is used.
XFF (X-Forwarded-For) Header¶
If STON is placed between the client and the origin server, the origin server will not be able to obtain the client’s IP. Therefore, all HTTP requests sent by STON to the origin server have an X-Forwarded-For header.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<XFFClientIPOnly>OFF</XFFClientIPOnly>
<XFFClientIPOnly>OFF (default)Appends the client’s IP to the XFF header sent by the client (IP: 128.134.9.1). If the client did not send an XFF header, only the client IP is displayed.X-Forwarded-For: 220.61.7.150, 61.1.9.100, 128.134.9.1
ONSends the first address of the XFF header to the origin server.X-Forwarded-For: 220.61.7.150
ETag Header Recognition¶
Configures the recognition of the ETag header returned by the origin server.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<OriginalETag>OFF</OriginalETag>
<OriginalETag>OFF (default)The ETag header is ignored.ONThe ETag header is recognized and an If-None-Match header is appended on content renewal.
Origin Request Header Modification¶
The HTTP header can be changed when sending HTTP requests to the origin server based on certain conditions.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<ModifyHeader FirstOnly="OFF">OFF</ModifyHeader>
<ModifyHeader>OFF (default)Keeps the original header.ONThe header changes based on conditions.
The point in time the header is changed is when the HTTP request packet is completed, just before it is sent to the origin server. However, range requests cannot be changed.
This function is a sub-function of Client Request/Response Header Modification. The $ORGREQ keyword is used for header changes.
# /svc/www.example.com/headers.txt
$URL[/*.mp4], $ORGREQ[x-media-type: video/mp4], set
$IP[1.1.1.1], $ORGREQ[user-agent: media_probe], put
*, $ORGREQ[If-Modified-Since], unset
*, $ORGREQ[If-None-Match], unset
Note
If the If-Modified-Since and If-None-Match headers are set to unset, content will always be downloaded when their TTL expires.
Redirect Tracking¶
If the origin server returns responses from the Redirect category (301, 302, 303, 307), the Location header is tracked to request content.
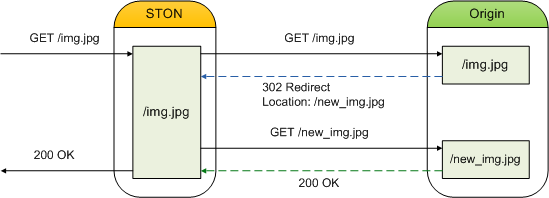
Clients will not know if they are redirected or not.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<RedirectionTrace>OFF</RedirectionTrace>
<RedirectionTrace>OFF (default)Saves as a 3xx response.ONDownloads content from the address given in the Location header. If the format of the header is incorrect or there is no header, then tracking will fail. In order to prevent infinite redirection, STON will only redirect once.