Chapter 17. Media¶
This chapter will explain how to intelligently handle media in the service. Due to there being various client environments and service diversity, there will be many cases where content must be processed in various ways. As such, identical content will exist on the origin server in different forms. This method will not just require more processing time and storage space, it is also hard to maintain.
Reordering MP4/M4A Header¶
Normally, the header of an MP4 file cannot be completed during the encoding process, and so is attached at the end of the file after encoding is done. An extra step is necessary to move the header to the front. If the header is at the end, Pseudo-Streaming will be unavailable for media players that do not support that format. However, reordering the header can easily allow for Pseudo-Streaming support.
The header reordering only occurs during the transfer stage and will not modify the original format. It will also not take up extra storage space.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Media>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Media>
<UpfrontMP4Header>OFF</UpfrontMP4Header>
<UpfrontM4AHeader>OFF</UpfrontM4AHeader>
<UpfrontMP4Header>OFF (default)Nothing happens.ONIf the extension is .mp4 and the header is at the end of the file, the header will be moved to the front of the file before transfer.
<UpfrontM4AHeader>OFF (default)Nothing happens.ONIf the extension is .m4a and the header is at the end of the file, the header will be moved to the front of the file before transfer.
If content with headers that need to be moved are being requested for the first time, the parts necessary for reordering will be downloaded first. This method is not only smart, but also occurs quickly. The client will receive the file as if the header had always been in the front, without having to see any of the complicated processes occurring backstage.
Note
If the file is broken or unable to be analyzed, it will be transferred as is.
Trimming¶
Extracts desired parts of a media file using time values. Trimming only occurs during the transfer stage and will not modify the original format. It will also not take up extra storage space.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Media>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Media>
<MP4Trimming StartParam="start" EndParam="end" AllTracks="off">OFF</MP4Trimming>
<M4ATrimming StartParam="start" EndParam="end" AllTracks="off">OFF</M4ATrimming>
<MP3Trimming StartParam="start" EndParam="end">OFF</MP3Trimming>
<MP4Trimming><MP3Trimming><M4ATrimming>OFF (default)Nothing happens.ONIf the extension matches (.mp4, .mp3, .m4a), the file will be trimmed to the desired section. The section to be trimmed can be configured with theStartParamandEndParamproperties.AllTrackspropertyOFF (default)Trims only audio/video tracks (Mod-H264 format).ONTrims all tracks. Media player compatibility must be checked before using this setting.
Parameters can input via client QueryStrings. For example, to trim a certain section of a 10-minute video clip, you would specify the desired times (unit: seconds) in QueryStrings.
http://vod.wineosoft.co.kr/video.mp4 // 10 minutes: trim entire video
http://vod.wineosoft.co.kr/video.mp4?end=60 // 1 minute: trim from start to 1 minute (60 seconds)
http://vod.wineosoft.co.kr/video.mp4?start=120 // 8 minutes: trim from 2 minutes (120 seconds) to end
http://vod.wineosoft.co.kr/video.mp4?start=3&end=13 // 10 minutes: trim from 3 seconds to 13 seconds
If the StartParam value is larger than the EndParam value, the section will be considered undefined. This function was developed to facilitate the Skip function for media players that support HTTP Pseudo-Streaming. As such, STON will recognize keyframes and times to extract the sections so the video can play properly, instead of trimming the file based on the offset, as when processing a Range request.
The file delivered to the client is in the form of a complete MP4 file with a recreated MP4 header, as shown below.
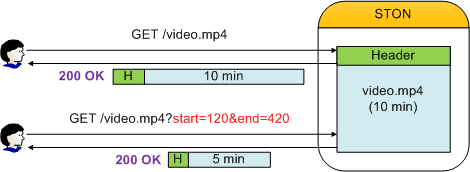
The file is transferred in the form of a complete file.
The extracted section is recognized as a separate file, so a 200 OK response is returned. If the Range header is specified as shown below, the Range will be calculated from the extracted file and a 206 Partial Content response is returned.
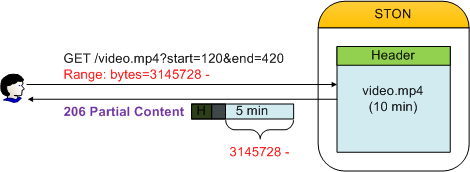
It is processed like a normal Range request.
Because trimming parameters use the QueryString format, there is a possibility for confusion with QueryString Differentiation. If <ApplyQueryString> is set to ON, the QueryStrings of URLs requested by clients will be recognized, but StartParam and EndParam will be removed.
GET /video.mp4?start=30&end=100
GET /video.mp4?tag=3277&start=30&end=100&date=20130726
In the above example, if start and end are entered for StartParam and EndParam, respectively, the values will only be used to extract a section and are removed when creating a Caching-Key or sending a request to the origin server. They will then be recognized as below.
GET /video.mp4
GET /video.mp4?tag=3277&date=20130726
Expansion modules and CDN solutions can also affect how QueryStrings are used.

Module/CDN references provided by the JW Player
In addition, the ngx_http_mp4_module in nginx and the Mod-H264-Streaming-Testing-Version2 in lighttpd use start as a QueryString.
Multi-Trimming¶
Multiple sections of a video clip are stitched into a single one using time values as a basis.
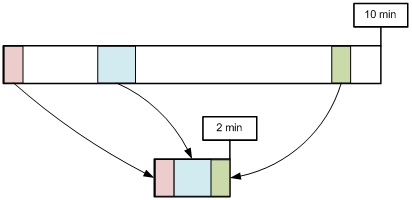
/video.mp4?trimming=0-30,210-270,525-555
The function behaves in much the same way as Trimming except for how the sections are chosen.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Media>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Media>
<MP4Trimming MultiParam="trimming" MaxRatio="50">OFF</MP4Trimming>
<M4ATrimming MultiParam="trimming">OFF</M4ATrimming>
<MP4Trimming><M4ATrimming>MultiParam (default: "trimming")The set name is used for the QueryString key to determine the sections to be extracted. Each section is represented by “start - end”, and separated by a comma (,).MaxRatio (default: 50%)The video trimmed by Multi-Trimming can only be as large as theMaxRatio (max: 100%)of the original video. Segments that exceed theMaxRatioare ignored.
For example, the following call will create a 3-minute video.
http://example.com/video.mp4?trimming=10-70,560-620,1245-1305
Videos can also be made with the same clip repeating, or the front and back switched.
http://example.com/video.mp4?trimming=17-20,17-20,17-20,17-20
http://example.com/video.mp4?trimming=1000-1200,500-623,1900-2000
http://example.com/video.mp4?trimming=600-,400-600
If the time values are not input, it will refer to the start and end times of the original video.
Note
Multi-Trimming takes priority over Trimming. If the Multi-Trimming key is seen in the QueryString, the Trimming key will be ignored.
MP4 HLS¶
MP4 files can be provided in the service with HTTP Live Streaming (HLS). The origin server no longer needs to split files for the HLS service. Regardless of the location of the MP4 file header, the file can be converted in real time to .m3u8/.ts while downloading the file.
Note
MP4HLS is not a transcoding that converts elementary streams (video or audio). Therefore, smooth playback is only possible for MP4 files encoded for HLS. If a file is not encoded for HLS, the video may freeze or the audio may not play. The video/audio encoding format given by Apple at the time of writing (2014/2/20) is shown below.
What are the specifics of the video and audio formats supported? Although the protocol specification does not limit the video and audio formats, the current Apple implementation supports the following formats:
[Video] H.264 Baseline Level 3.0, Baseline Level 3.1, Main Level 3.1, and High Profile Level 4.1.
[Audio] HE-AAC or AAC-LC up to 48 kHz, stereo audio MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3) 8 kHz to 48 kHz, stereo audio AC-3 (for Apple TV, in pass-through mode only)
Note: iPad, iPhone 3G, and iPod touch (2nd generation and later) support H.264 Baseline 3.1. If your app runs on older versions of iPhone or iPod touch, however, you should use H.264 Baseline 3.0 for compatibility. If your content is intended solely for iPad, Apple TV, iPhone 4 and later, and Mac OS X computers, you should use Main Level 3.1.
For existing methods, the following origin files are necessary for Pseudo-Streaming and HLS. In this case, STON will copy the origin files as is and provide them to the clients. However, as the play time gets longer, more derivative files will be created, making it harder to manage.
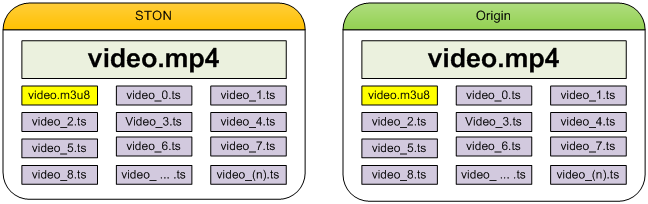
A laborious way to provide HLS
Meanwhile, <MP4HLS> can dynamically create the necessary files from the original for the HLS service.
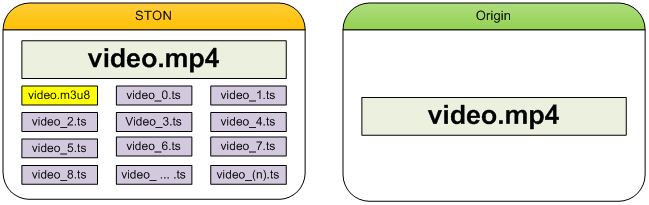
A smarter way to provide HLS
All .m3u8/.ts files will be derived from the original file and will not consume any extra storage space. The file will only temporarily be created in memory when in use, and automatically discarded when not in use.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Media>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Media>
<MP4HLS Status="Inactive" Keyword="mp4hls">
<Index Ver="3" Alternates="off">index.m3u8</Index>
<Sequence>0</Sequence>
<Duration>10</Duration>
<AlternatesName>playlist.m3u8</AlternatesName>
</MP4HLS>
<MP4HLS>Status (default: Inactive)Active only when set toActive.Keyword (default: mp4hls)HLS service keyword.
<Index> (default: index.m3u8)HLS index file name (.m3u8).Ver (default: 3)Index file version. If the version is 3, the header will be specified as#EXT-X-VERSION:3and the time value of#EXTINFwill be given to the third decimal. If the version is 1, there is no#EXT-X-VERSIONheader, and the time value of#EXTINFis rounded up to a whole number.Alternates (default: OFF)Turns Stream Alternates on or off.
OFF. The TS list is provided by
<Index>.
ON. The TS list is provided by
<AlternatesName>.
<Sequence> (default: 0)The starting number for .ts files. The number will start with the given value and increment by 1 with every file.<Duration> (default: 10 s)Splits the MP4 file for HLS with the given time (in seconds). The basis for splitting are the keyframes in video/audio. Because the keyframes can be uneven, equal splitting is not always possible. If you attempt to split using 10 seconds but either 9 or 12 seconds is possible due to the keyframes, the closer value (9 seconds) will be chosen.<AlternatesName> (default: playlist.m3u8)Stream Alternates file name.http://www.example.com/video.mp4/mp4hls/playlist.m3u8
For example, if the service address is as follows, Pseudo-Streaming can be performed with this address.
http://www.example.com/video.mp4
The virtual host will use the configured Keyword in <MP4HLS> to perform the HLS service. If the following URL is called, an index.m3u8 file will be created from /video.mp4.
http://www.example.com/video.mp4/mp4hls/index.m3u8
If the Alternates property is set to ON, the <Index> file will provide the <AlternatesName> file in the service.
#EXTM3U
#EXT-X-VERSION:3
#EXT-X-STREAM-INF:PROGRAM-ID=1,BANDWIDTH=200000,RESOLUTION=720x480
/video.mp4/mp4hls/playlist.m3u8
The Bandwidth and Resolution in #EXT-X-STREAM-INF are provided dynamically by analyzing the video.
Note
Though Stream Alternates is provided, index.m3u8 in the current version will always provide only one sub-index file (playlist.m3u8). This is because the cache can’t tell that video_1080.mp4 and video_720.mp4 are the same video (with only the encoding being different).
The final .ts list (version 3) that is created is as follows.
#EXTM3U
#EXT-X-TARGETDURATION:10
#EXT-X-VERSION:3
#EXT-X-MEDIA-SEQUENCE:0
#EXTINF:11.637,
/video.mp4/mp4hls/0.ts
#EXTINF:10.092,
/video.mp4/mp4hls/1.ts
#EXTINF:10.112,
/video.mp4/mp4hls/2.ts
... (omitted)...
#EXTINF:10.847,
/video.mp4/mp4hls/161.ts
#EXTINF:9.078,
/video.mp4/mp4hls/162.ts
#EXT-X-ENDLIST
There are three policies for splitting.
- If the keyframe interval is smaller than
<Duration>If the keyframe is 3 seconds and<Duration>is 20 seconds, the largest multiple of the 3 (the keyframe) that does not exceed 20 (the duration) will be used to split the video (in this case, 18). - If the keyframe interval is close to
<Duration>If the keyframe is 9 seconds and<Duration>is 10 seconds, the largest multiple of the 9 (the keyframe) that does not exceed 10 (the duration) will be used to split the video (in this case, 9). - If the keyframe interval is larger than
<Duration>The keyframe interval is used to split the video.
Let’s understand how STON will behave according to the following client request.
GET /video.mp4/mp4hls/99.ts HTTP/1.1
Range: bytes=0-512000
Host: www.winesoft.com
STONInitial loading. (Nothing has been cached yet.)ClientHTTP Range request. (Requests the first 500 KB of the 100th file.)STONCreates a caching object of the /video.mp4 file.STONDownloads from the origin server the portion necessary to analyze the /video.mp4 file.STONDownloads from the origin server the portion necessary to provide the 100th file (99.ts).STONCreates the 100th file (99.ts) and proceeds with the Range service.STONDiscards the 99.ts file after completing the service.
Note
If MP4Trimming is set to ON, MP4 files that have been trimmed can also be converted to HLS. (HLS video files cannot be trimmed. Note that HLS is not MP4 but MPEG2TS.) The most natural way of converting a trimmed video to HLS is the following.
/video.mp4?start=0&end=60/mp4hls/index.m3u8
Though this will not cause any problems, it is HTTP policy to put the QueryString at the end. To adhere to this policy, the following forms will produce the same effect.
/video.mp4/mp4hls/index.m3u8?start=0&end=60
/video.mp4?start=0/mp4hls/index.m3u8?end=60
MP3 HLS¶
MP3 files can also be provided in the service with HLS.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Media>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Media>
<MP3HLS Status="Inactive" Keyword="mp3hls">
<Index Ver="3" Alternates="off">index.m3u8</Index>
<Sequence>0</Sequence>
<Duration>10</Duration>
<AlternatesName>playlist.m3u8</AlternatesName>
</MP3HLS>
All settings and behaviors are identical to MP4 HLS.
DIMS¶
The Dynamic Image Management System (DIMS) is a function that can process images into various other forms. DIMS is an expansion based on mod_dims. A total of seven forms (optimize, crop, thumbnail, resize, reformat, quality, composite) are available and can also be combined.
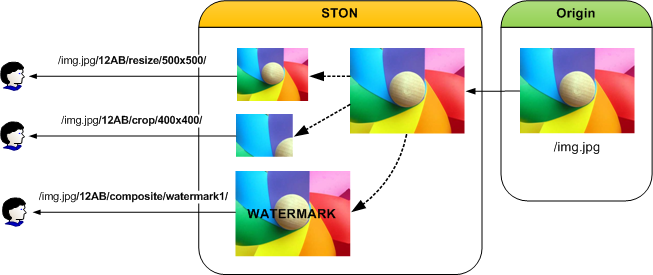
Various ways of image processing
The image is generated dynamically and can be called by placing the keyword and the processing option at the end of the URL. The processed image will be cached and will not be reprocessed as long as the original image is not changed.
For example, if the original file is /img.jpg, the following formats can be used to process the image. (“12AB” is the configured keyword.)
http://image.example.com/img.jpg // Original image
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/12AB/optimize
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/12AB/resize/500x500/
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/12AB/crop/400x400/
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/12AB/composite/watermark1/
If <Dims> is not specifically configured, none of the following will be activated.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<Dims Status="Active" Keyword="dims" MaxSourceSize="10" OnFailure="message" />
<Dims>StatusDIMS activation (ActiveorInactive).KeywordThe keyword to differentiate between the original and DIMS.MaxSourceSize (default: 10 MB)Maximum original image size (in MB).OnFailureBehavior when image conversion fails.message (default)Responds with a 500 Internal Error. A more specific error message will be included.The original file was not successfully downloaded.The original file size is too large.The original file loading failed.Image converting failed or invalid DIMS command.
redirectPerforms a 302 Redirect to the original image URL.
Optimization¶
Optimization reduces the size of the image file while maintaining its quality. Only JPEG, JPEG-2000, and Lossless-JPEG file formats are supported. Images that have already been optimized by another tool will most likely be unable to be optimized further.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/optimize
Optimization does not require any extra options besides the keyword. As such, it is suggested to place it at the very end when combining with other options.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/resize/100x100/optimize
All the other DIMS functions use a lot of system resources, but optimization is the most resource-intensive process. The following is the result of a performance test with various images with a HitRatio of 0%.
OSCentOS 6.2 (Linux version 2.6.32-220.el6.x86_64 (mockbuild@c6b18n3.bsys.dev.centos.org) (gcc version 4.4.6 20110731 (Red Hat 4.4.6-3) (GCC) ) #1 SMP Tue Dec 6 19:48:22 GMT 2011)CPUIntel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E3-1230 v3 @ 3.30GHz (8 processors)RAM16GBHDDSMC2108 SAS 275GB X 3EA
| Size | Conversion | Response time (ms) | Client traffic (Mbps) | Origin traffic (Mbps) | Traffic reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16KB | 720 | 19.32 | 46.32 | 92.62 | 49.99 |
| 32KB | 680 | 20.68 | 86.42 | 165.08 | 47.65 |
| 64KB | 285 | 50.16 | 80.67 | 150.96 | 46.56 |
| 128KB | 274 | 57.80 | 164.35 | 276.52 | 40.56 |
| 256KB | 210 | 80.74 | 99.42 | 432.35 | 77.00 |
| 512KB | 113 | 156.18 | 160.54 | 436.04 | 63.18 |
| 1MB | 20 | 981.07 | 90.62 | 179.88 | 49.62 |
With about a 50% reduction in traffic, the function is very effective. As stated before, optimization is a very resource-intensive process. As can be seen in the above table, the size of the file is the most important variable.
Because of this, applying optimization without careful consideration can cause huge problems. A situation with a good Request hit ratio is recommended; otherwise, you must make sure that there are enough CPU resources in accordance with the scale of the service.
Crop¶
With the upper left corner as the origin, the image is cropped to the desired dimensions. The dimensions are formatted as widthxheight{+-}x{+-}y{%}. The following is an example of cropping a section of width=100, height=200 starting from x=20, y=30.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/crop/100x200+20+30/
Generating Thumbnails¶
This function generates thumbnails. The size and options are formatted as widthxheight{%} {@} {!} {<} {>}. In general, the width and height of the original image are used as the maximum values for the function. Whether the image is being enlarged or shrunk, the aspect ratio will always be preserved. To resize an image to a specific size, an exclamation point (!) can be added to the end of the size. For example, 640X480! means that a thumbnail of exactly size 640x480 will be generated. If either the width or the height is omitted, the omitted value will be automatically calculated based on the aspect ratio.
For example, /thumbnail/100/ will determine the height of the thumbnail using the width, while /thumbnail/x200/ will determine the width using the height. The thumbnail size can also be expressed as a percentage (%) of the original image. To enlarge the image, a value larger than 100 (e.g. 125%) is used, while a value lower than 100 will shrink the image. It is important to keep in mind that the % character is encoded as %25 in the URL Encoding policy.
For example, 50% is encoded as 50%25. The following example generates a thumbnail with width=78, height=110.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/thumbnail/78x110/
Resizing¶
This function changes the size of the image. The new size is formatted as width x height. Even if the image is changed, the aspect ratio will be preserved. The following example resizes the original image to a size of width=200, height=200.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/resize/200x200/
Converting Format¶
This function converts the format of the image. The supported formats are “png”, “jpg”, and “gif”. The following example converts from a JPG to a PNG.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/format/png/
Adjusting Image Quality¶
This function adjusts the image quality. This function is effective because it can reduce the volume of the transferring image. The allowed range is from 0 to 100. The following example adjusts the quality of an image to 25%.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/quality/25/
Image Composition¶
This function composites two or more images. Unlike the previous functions, the settings for this function must be configured in advanced. This function is helpful when placing a watermark on an image.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<Dims Status="Active" Keyword="dims" port="8500">
<Composite Name="water1" File="/img/small.jpg" />
<Composite Name="water2" File="/img/medium.jpg" Gravity="se" Geometry="+0+0" Dissolve="50" />
<Composite Name="water_ratio" File="/img/wmark_s.png" Gravity="s" Geometry="+0+15%" Dissolve="100" />
</Dims>
<Composite>Configures the settings for image composition. The function is configured by its properties, and will take no extra values.
NameDesignates the name of the image to be called. The “/” character cannot be used. This option will be located after “/composite/” in the URL.FileDesignates the path of the image to be composited.Gravity (default: c)Starting from the upper left, there are nine points (nw, n, ne, w, c, e, sw, s, se) where composition can be applied.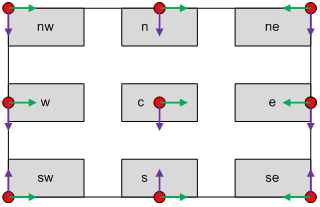
Gravity reference points
Geometry (default: +0+0)Uses
Gravityas the origin to determine the location where composition is applied. The format is {+-}x{+-}y. The red circles are the points specified by the Gravity property and +0+0, and can be moved towards the center of the image as the values of +x+y increase. The green arrow indicates +x, and the purple arrow indicates +y. If -x-y is used, it will refer to a point outside of the image dimensions, and the composited image will not show up. This property may seem rather convoluted, but because it can automatically calculate the size of images, it is effective in creating consistent results. Furthermore, the % option can be used as in +x%+y% to use ratios as values.
Dissolve (default: 50)Opacity of the image to be composited (0~100).
If <Composite> is configured, the Name property can be called to composite the images.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/composite/water1/
Original Image Conditions¶
Options will be dynamically applied in different ways based on the conditions of the original image. For example, if you want to lower the quality to 50% for images that are smaller than 1024x768 and resize images to 1024x768 for images that are larger, you can configure <ByOriginal> as follows.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<Dims Status="Active" Keyword="dims" port="8500">
<ByOriginal Name="size1">
<Condition Width="1024" Height="768">/quality/50/</Condition>
<Condition>/resize/1024x768/</Condition>
</ByOriginal>
</Dims>
<ByOriginal>Called with theNameproperty. Various conditions can be configured below with<Condition>.<Condition>Changes will be applied to images that satisfy the conditions.WidthIf the width is smaller than the set value, the change is applied.HeightIf the height is smaller than the set value, the change is applied.
If no conditions are set, changes will be applied regardless of the image size.
<Condition> tags are applied in the order they are configured. Therefore, the condition for smaller images should be set first. This can be called with the following.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/byoriginal/size1/
For another example, different <Composite> conditions can be made for different image sizes. In this case, the following example uses the different Name``s of ``<Composite>.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<Dims Status="Active" Keyword="dims" port="8500">
<Composite Name="water1" File="/img/small.jpg" />
<Composite Name="water2" File="/img/medium.jpg" Gravity="se" Geometry="+0+0" Dissolve="50" />
<Composite Name="water3" File="/img/big.jpg" Gravity="se" Geometry="+10+10" Dissolve="50" />
<ByOriginal Name="size_water">
<Condition Width="400">/composite/water1/</Condition>
<Condition Width="800">/composite/water2/</Condition>
<Condition>/composite/water3/</Condition>
</ByOriginal>
</Dims>
When called with the following, a different composite will be made depending on the image size.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/byoriginal/size_water/
Animated GIF¶
All DIMS conversions apply identically to animated GIFs. The order of processing is as follows.
- The frames of the GIF are loaded as multiple images.
- Each image is converted.
- The converted frames are put back together in a single GIF.
The more frames there are, the more processing there needs to be done, which can lower service quality. In this case, you can configure the process to convert only the first frame, lowering the cost of processing.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<Dims FirstFrameOnly="OFF" />
FirstFrameOnly (default: OFF)When set to ON, only the first frame of the animated GIF is converted.
If the following URL is called, the FirstFrameOnly can be specifically designated as well.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/firstframeonly/on/resize/200x200/
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/firstframeonly/off/resize/200x200/
If called with the URL above, it will take precedence over the configuration.
Other¶
The above default functions can be combined to process images in more complex ways. For example, you can generate a thumbnail (78x110), convert the format from JPG to PNG, and change the quality to 50% all in one step.
http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/thumbnail/78x110/format/png/quality/50/
DIMS can process images using URL calls. As such, it is important to take note of other options that can affect URLs and cause unwanted results.
If QueryString Differentiation is set to
OFF, QueryStrings found after keywords are ignored.http://image.example.com/img.jpg?session=5234&type=37/dims/resize/200x200/ If it is set to ``ON``, it will be understood as is, but if it is set to ``OFF``, the URL will be understood as the following. :: http://image.example.com/img.jpg/dims/resize/200x200/
If Case Sensitivity is set to
OFF, all URLs will be converted to lowercase and then processed. Therefore, if DIMS keywords contain uppercase letters, they will not be recognized when called. It is recommended to always use only lowercase letters for keywords.