Chapter 6. Handling HTTP Requests¶
This chapter will explain the HTTP client session and methods of handling HTTP requests. Parts of this chapter may be difficult to follow without some understanding of HTTP. However, as these functions are not critical to the service, you can simply use the default settings without affecting the quality of service at all.
Session Management¶
An HTTP session is created when an HTTP client connects to the STON server. Content saved on the server is delivered to the client through the HTTP session. The process from the request to the response is called an HTTP transaction. An HTTP session handles multiple HTTP transactions in succession.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<ConnectionHeader>keep-alive</ConnectionHeader>
<ClientKeepAliveSec>10</ClientKeepAliveSec>
<KeepAliveHeader Max="0">ON</KeepAliveHeader>
<ConnectionHeader> (default: keep-alive)Configures the Connection header (keep-aliveorclose) of the HTTP response sent to the client.<ClientKeepAliveSec> (default: 10 sec)Terminates a session when there is no transaction with the client session for the given amount of time. If the time is set to too large a value, then the number of sessions that are not transacting can grow unexpectedly. Maintaining a large number of sessions can cause load on the system.<KeepAliveHeader>ON (default)Specifies the Keep-Alive header in the HTTP response. IfMax (default: 0)is set to greater than zero, then theMaxvalue will be used for the Keep-Alive header. Each HTTP transaction will reduce the value by one.OFFOmits the Keep-Alive header in the HTTP response.
HTTP Session Maintenance Polices¶
STON follows Apache policies as much as possible. Specifically, there are many variables in the session maintenance policies based on the value of the HTTP header. The following is a list of items that can influence HTTP session maintenance policies.
- The Connection header specified in the HTTP response (“Keep-Alive” or “Close”)
- Virtual host
<Connection>setting - Virtual host session Keep-Alive time setting
- Virtual host
<Keep-Alive>setting
When “Connection: Close” is specified in the client HTTP request:
GET / HTTP/1.1 ...(omitted)... Connection: Close
For an HTTP request like this, a “Connection: Close” response will be returned regardless of the virtual host settings. The Keep-Alive header will not be specified.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...(omitted)... Connection: Close
When this HTTP transaction is completed, the connection is terminated.
When
<ConnectionHeader>is set toClose:# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options> # vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options> <ConnectionHeader>Close</ConnectionHeader>
A “Connection: Close” response will be returned regardless of the client’s HTTP requests. The Keep-Alive header will not be specified.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...(omitted)... Connection: Close
When
<KeepAliveHeader>is set toOFF:# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options> # vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options> <ConnectionHeader>Keep-Alive</ConnectionHeader> <KeepAliveHeader>OFF</KeepAliveHeader>
The Keep-Alive header will not be specified. The HTTP session can be continuously reused.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...(omitted)... Connection: Keep-Alive
When
<KeepAliveHeader>is set toON:# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options> # vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options> <ConnectionHeader>Keep-Alive</ConnectionHeader> <ClientKeepAliveSec>10</ClientKeepAliveSec> <KeepAliveHeader>ON</KeepAliveHeader>
The Keep-Alive header will be specified. The Keep-Alive time setting of the session is used for the timeout value.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...(omitted)... Connection: Keep-Alive Keep-Alive: timeout=10
Note
The Relationship between
<Keep-Alive>and<ClientKeepAliveSec>The
<Keep-Alive>setting references the<ClientKeepAliveSec>setting, but<ClientKeepAliveSec>is related to a more fundamental problem. The most important issue in terms of performance or resources is the issue of when to terminate idle sessions, or sessions where HTTP transactions are no longer occurring. HTTP header settings can be changed dynamically and can occasionally be omitted, but the termination of idle sessions is a more complicated problem. Because of this,<ClientKeepAliveSec>is not unified with<KeepAliveHeader>and exists separately.When the
Maxproperty of<KeepAliveHeader>is set:# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options> # vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options> <ConnectionHeader>Keep-Alive</ConnectionHeader> <ClientKeepAliveSec>10</ClientKeepAliveSec> <KeepAliveHeader Max="50">ON</KeepAliveHeader>
The max value will be specified in the Keep-Alive header. The session can be used for the number set by the
Maxproperty, and each HTTP transaction will decrease the value by one.HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...(omitted)... Connection: Keep-Alive Keep-Alive: timeout=10, max=50
When the max value of Keep-Alive runs out:
As mentioned above, if the max value is set, it will gradually decrease until it hits one.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...(omitted)... Connection: Keep-Alive Keep-Alive: timeout=10, max=1
This means that only one more HTTP transaction is possible in the current session. After one more HTTP request, the response will be “Connection: Close” as shown below.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...(omitted)... Connection: Close
Client Cache-Control¶
This section covers the settings related to client cache-control.
Age Header¶
The age header stands for the elapsed time (in seconds) from the moment something is cached, ans is calculated by RFC2616 - 13.2.3 Age Calculations.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<AgeHeader>OFF</AgeHeader>
<AgeHeader>OFF (default)Omits Age header.ONSpecifies Age header.
Expires Header¶
The following refreshes the Expires header.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<RefreshExpiresHeader Base="Access">OFF</RefreshExpiresHeader>
<RefreshExpiresHeader>OFF (default)Specifies the Expires header returned by the origin server to the client. If the Expires header is omitted in the origin server, it will also be omitted in the response to the client.ONThe Expires conditions will be reflected in the Expires header. TheOFFsetting will be applied for content that does not satisfy the conditions.
The Expires condition behaves identically to the mod_expires of Apache. You can also configure the Expires header and Cache-Control values of content that matches special conditions (such as URL or MIME Type). The max-age value of the Cache-Control is the difference between the given Expires time and the requested time.
The Expires conditions can be set in /svc/{virtual host name}/expires.txt.
# /svc/www.exmaple.com/expires.txt
# The delimiter is a comma (,), and the format is {condition},{time},{reference}.
$URL[/test.jpg], 86400
/test.jpg, 86400
*, 86400, access
/test/1.gif, 60 sec
/test/*.dat, 30 min, modification
$MIME[application/shockwave], 1 years
$MIME[application/octet-stream], 7 weeks, modification
$MIME[image/gif], 3600, modification
- Condition
The condition can be set to either a URL or a MIME Type. $URL[…] is used for URL, and $MIME[…] is used for MIME Type. Patterned expressions can also be used, and if the $ format is not used, the condition will be recognized as a URL.
- Time
Sets the Expires expiration time. Common units of time are supported, and if the units are not specified, seconds will be used.
- Reference
Configures the reference point for the Expires expiration time. If a separate reference point is not specified, then it will use the Access as a reference. Access uses the current time as a reference. The following example indicates that for files that have a MIME Type of image/gif, the Expires header value will be set to 1 day and 12 hours after the access time.
$MIME[image/gif], 1 day 12 hours, access
Modification uses the Last-Modified time sent by the origin server as a reference. The following example indicates that for all JPG files, the Expires value will be set to 30 minutes after the Last-Modified time.
*.jpg, 30 min, modification
For Modification, if the calculated time turns out to be in the past relative to the current time, then the current time is used. If the origin server does not provide a Last-Modified header, then an Expires header will not be sent.
ETag Header¶
The ETag header in the HTTP response sent to the client can be configured.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<ETagHeader>ON</ETagHeader>
<ETagHeader>ON (default)Specified ETag header.OFFOmits ETag header.
Response Headers¶
Origin Nonstandard Header¶
For the sake of performance and security, out of the headers sent by the origin server, only the standard headers will be recognized.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<OriginalHeader>OFF</OriginalHeader>
<OriginalHeader>OFF (default)Ignores nonstandard headers.ONSaves all headers (with the exception of cookie, set-cookie, and set-cookie2) and sends them to the client. However, this option can consume more memory.
Via Header¶
The Via header in the HTTP response sent to the client can be configured.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<ViaHeader>ON</ViaHeader>
<ViaHeader>ON (default)Specifies the Via header as follows.Via: STON/2.0.0
OFFOmits the Via header.
Server Header¶
The Server header in the HTTP response sent to the client can be configured.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<ServerHeader>ON</ServerHeader>
<ServerHeader>ON (default)Specifies the Server header of the origin server.OFFOmits the Server header.
Client Request/Response Header Modification¶
The client’s requests and responses can be modified based on certain conditions.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<ModifyHeader FirstOnly="OFF">OFF</ModifyHeader>
<ModifyHeader>OFF (default)Does not modify.ONModifies the header based on the header modification conditions.
The following explains the points when the header is modified.
- HTTP Request Header Modification Point
- The header is modified when the client’s HTTP request is first recognized. If the header gets modified, then it will be handled in its modified state by the cache module. However, the Host header cannot have its URI modified.
- HTTP Response Header Modification Point
- The header is modified just before the response to the client. However, the Content-Length cannot be changed.
Header modification conditions can be set in /svc/{virtual host name}/headers.txt. Multiple conditions can be set, and if header meets all the conditions, then all modifications will be applied in order.
If only the first condition should be applied, then the FirstOnly property should be set to ON. If different conditions attempt to modify the same header, then the result will be Last-Win from set or specified by put or append.
# /svc/www.example.com/headers.txt
# The delimiter is a comma (,).
# Request Modification
# The format is {Match}, {$REQ}, {Action(set|put|append|unset)}.
$IP[192.168.1.1], $REQ[SOAPAction], unset
$IP[192.168.2.1-255], $REQ[accept-encoding: gzip], set
$IP[192.168.3.0/24], $REQ[cache-control: no-cache], append
$IP[192.168.4.0/255.255.255.0], $REQ[x-custom-header], unset
$IP[AP], $REQ[X-Forwarded-For], unset
$HEADER[user-agent: *IE6*], $REQ[accept-encoding], unset
$HEADER[via], $REQ[via], unset
$URL[/source/*.zip], $REQ[accept-encoding: deflate], set
# Response Modification
# The format is {Match}, {$RES}, {Action(set|put|append|unset)}, {condition}.
# {condition} can modify the header based on special response codes, but is not mandatory.
$IP[192.168.1.1], $RES[via: STON for CDN], set
$IP[192.168.2.1-255], $RES[X-Cache], unset, 200
$IP[192.168.3.0/24], $RES[cache-control: no-cache, private], append, 3xx
$IP[192.168.4.0/255.255.255.0], $RES[x-custom-header], unset
$HEADER[user-agent: *IE6*], $RES[vary], unset
$HEADER[x-custom-header], $RES[cache-control: no-cache, private], append, 5xx
$URL[/source/*], $RES[cache-control: no-cache], set, 404
/secure/*.dat, $RES[x-custom], unset, 200
/*.mp4, $RES[Access-Control-Allow-Origin: example1.com], set
/*.mp4, $RES[Access-Control-Allow-Origin: example2.com], put
{Match} can be set to IP, GeoIP, Header, and URL forms.
- IP The format is $IP[…] and supports the formats of IP, IP Range, Bitmask, and Subnet.
- GeoIP The format is $IP[…] and GeoIP must be configured in advance. The country codes ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 and ISO 3166-1 alpha-3 are permitted.
- Header The format $HEADER[Key : Value]. The Value can be either a specific expression or a pattern. If the Value is omitted, the condition will be the existence of a header corresponding to the Key.
- URL The format is $URL[…] and can be omitted. It can be either a specific expression or a pattern.
{$REQ} and {$RES} configure how to modify the header. set, put, and append configure the header to {Key: Value}, and if the Value is omitted, an empty value (“”) will be input. unset will only input the {Key}.
{Action} can be set to one of the four settings: set , put , append , unset.
setThe Key and Value defined in the request/response header is added to the header. If the same Key is used, the new Value overwrites the old.put(resemblesset) If the same Key is used, the new Value is added in a new line instead of overwriting the old Value.append(resemblesset) If the same Key is used, the old Value and the new Value are attached with a comma (,).unsetThe Key defined in the request/response header is deleted from the header.
{Condition} can be set to a specific response code like 200 or 304 or can be set to a group of codes like 2xx, 3xx, 4xx, or 5xx. If {Match} matches but {Condition} does not, then the modification does not take place. If {Condition} is omitted, the response code is not checked.
URL Preprocessing¶
Regular expressions are used to modify the requested URLs. If URL preprocessing is defined, all client requests (HTTP or File I/O) must pass through the URL Rewriter.

The request can only reach the virtual host by passing through the URL Rewriter.
If an approaching Host name is modified by the URL Rewriter, then it will consider it as if the Host header was modified by the client’s HTTP request. URL preprocessing is configured in the virtual host settings (vhosts.xml). While most settings are under the virtual host, URL preprocessing can change the name of the Host requested by the client, so the settings must be on the same level as the virtual host.
# vhosts.xml
<Vhosts>
<Vhost ...> ... </Vhost>
<Vhost ...> ... </Vhost>
<URLRewrite ...> ... </URLRewrite>
<URLRewrite ...> ... </URLRewrite>
</Vhosts>
Multiple configurations are allowed, and the regular expressions will be checked in order.
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts>
<URLRewrite AccessLog="Replace">
<Pattern>www.example.com/([^/]+)/(.*)</Pattern>
<Replace>#1.example.com/#2</Replace>
</URLRewrite>
<URLRewrite>Configures URL preprocessing.
AccessLog (default: Replace)Configures URLs that will be recorded in the Access log.Replacerecords URLs after processing (/logo.jpg), whilePatternrecords URLs after processing (/baseball/logo.jpg).
Compression¶
STON can compress and deliver content in place of the origin server. Content must be categorized by the Accept-Encoding Header.
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
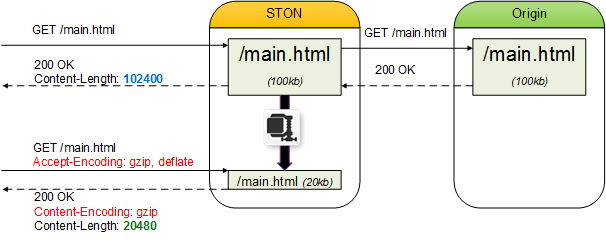
Files are compressed and delivered in real time.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<Compression Method="gzip" Level="6" SourceSize="2-2048">OFF</Compression>
<Compression>OFF (default)The compression function is not used.ONThe compression function is used with the following properties.Method (default: gzip)Assigns the compression method. For now, only gzip is supported.Level (default: 6)Assigns the compression level. This value varies based on theMethodused. Only 1~9 are available for gzip. A lower number means compression is faster but worse, while a higher number means compression is slower but better.SourceSize (default: 2-2048, unit: KB)Assigns a range for the source size. If files are too small, then files might be hardly compressed, while if files are too big, too much CPU might be consumed.
Compressed content is recognized and stored separately from the original content, and requests for the same content will not cause the content to be compressed again. The files to be compressed can be configured in /svc/{virtual host name}/compression.txt. The files will be compressed in that order.
# /svc/www.example.com/compression.txt
# The delimiter is a comma (,).
# The format is {URL condition}, {Method}, {Level}.
/sample.css, no // No compression
*.css // Compress *.css with default method and level
*.htm, gzip // Compress *.html with gzip (default level)
*.xml, , 9 // Compress *.xml with level 9 (default method)
*.js, gzip, 5 // Compress *.js with gzip level 5.
Compression is a function that consumes a large amount of CPU. The following is a performance test done on gzip (level 9) with files of different sizes.
OSCentOS 6.3 (Linux version 2.6.32-279.el6.x86_64 (mockbuild@c6b9.bsys.dev.centos.org) (gcc version 4.4.6 20120305(Red Hat 4.4.6-4) (GCC) ) #1 SMP Fri Jun 22 12:19:21 UTC 2012)CPUIntel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2603 0 @ 1.80GHz (8 processors)RAM8GBHDDSAS 275GB X 5EA
| Size | Comp. Ratio(%) | Files | Latency(ms) | Client Traffic(Mbps) | Origin Traffic(Mbps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1KB | 26.25 | 5288 | 6.72 | 40.58 | 55.02 |
| 2KB | 57.45 | 5238 | 7.20 | 41.52 | 97.58 |
| 4KB | 76.94 | 5236 | 7.18 | 42.44 | 184.04 |
| 8KB | 87.61 | 5021 | 7.53 | 41.87 | 337.80 |
| 16KB | 93.32 | 4608 | 8.30 | 41.19 | 616.83 |
| 32KB | 96.26 | 3495 | 13.55 | 34.53 | 924.22 |
| 64KB | 97.79 | 1783 | 24.50 | 20.71 | 938.83 |
| bootstrap.css(20KB) | 86.87 | 3944 | 9.67 | 83.79 | 638.25 |
| bootstrap.min.js(36KB) | 73.00 | 1791 | 51.50 | 139.00 | 514.86 |
If <Compression> is turned on, only uncompressed files will be requested from the origin server. In other words, the responses from the origin server will be to requests that have omitted the Accept-Encoding header. If the origin server specifies a Content-Encoding header to a request for uncompressed content, STON will recognize the content as already compressed and will not compress it again.
Note
Content that is already compressed on the origin server that matches <Compression> conditions may be compressed again. Since this can cause problems, this policy is followed.
- New content will be compressed.
- If the content is compressed on the origin server, it will not be compressed again.
- If the content is not compressed on the origin server, the corresponding content will be purged and compressed again.