Chapter 8. Bypass (Pass-through)¶
This chapter will explain how to set a bypass that delegates client request handling to the origin server. Bypasses can be divided into conditions and behaviors.
Bypass takes priority over the caching policy. If a service did not consider the edge server during the design state, it most likely cannot distinguish between static and dynamic resources. In this case, it can be configured so that all client requests are bypassed, caching only content that is frequently requested according to the log. In general, even a few hours of logging can dramatically decrease the load on the origin server. The real-time information provided by Chapter 10. Monitoring & Statistics is there to allow you to tune the service in real time.
Bypasses are not only fast, but they also work on the level of HTTP transactions. No matter how personalized a site is, it will generally be composed of a main page (.html) that changes dynamically, with the remaining 99% being made up of statis resources. A bypass version of Origin Request Default Header exists separately to match up with the actions of the origin server.
No-Cache Request Bypass¶
If the client sends a no-cache request, it will be bypassed.
GET / HTTP/1.1
cache-control: no-cache or cache-control:max-age=0
pragma: no-cache
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<BypassNoCacheRequest>OFF</BypassNoCacheRequest>
<BypassNoCacheRequest>OFF (default)The request is handled by the cache module.ONThe request is bypassed to the origin server.
Note
This setting is judged by the client’s action (likely Ctrl+F5). As a result, a large number of bypasses can cause strain on the origin server.
GET/POST Bypass¶
A bypass can be set to be the default action of GET/POST requests. It is important to keep in mind that because GET and POST are used differently, their actions will be different as well.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<BypassPostRequest>ON</BypassPostRequest>
<BypassGetRequest>OFF</BypassGetRequest>
<BypassPostRequest>ON (default)The POST request is bypassed to the origin server.OFFThe POST request is handled by STON.
<BypassGetRequest>OFF (default)The GET request is handled by STON.ONThe GET request is bypassed to the origin server.
Bypasses support the same conditions as Virtual Host ACL. Exception cases for bypasses can be set in /svc/{virtual host name}/bypass.txt.
# /svc/www.example.com/bypass.txt
$IP[192.168.2.1-255]
/index.html
If cache or bypass conditions are not specified, the opposite of the default setting will be applied. For example, if <BypassGetRequest> is set to ON, the exception cases become the caching list. There is a lot of room for confusion, but the second parameter can be set to explicitly state the conditions.
# /svc/www.winesoft.co.kr/bypass.txt
$HEADER[cookie: *ILLEGAL*], cache // Always cache
!HEADER[referer:] // Depends on the default setting
!HEADER[referer] & !HEADER[user-agent], bypass // Always bypass
$URL[/source/public.zip] // Depends on the default setting
The priority of actions is as follows.
- No-Cache bypass
- Bypass is specified in bypass.txt
- Default setting of bypass.txt
Fixed Origin Servers¶
Some transactions, such as login status, require a one-to-one communication between the origin server and the client. Properties of GET/POST Bypass can be used to fix the origin server to the client.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<BypassPostRequest OriginAffinity="ON">...</BypassPostRequest>
<BypassGetRequest OriginAffinity="ON">...</BypassGetRequest>
OriginAffinityON (default)Guarantees that the client’s requests will always be bypassed to the same origin server. However, it is not guaranteed to be the same socket.There is always the possibility that all the sockets of an origin server will lose connection. However, if this occurs, a new socket connection will simply be requested from the corresponding server.
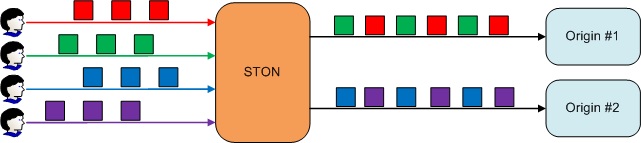
Requests will always be bypassed to the same server.
If the origin server being bypassed to ends up being excluded due to errors or dropped from DNS, requests will be bypassed to a new server instead.
OFFWill not guarantee which server the client requests will bypass to.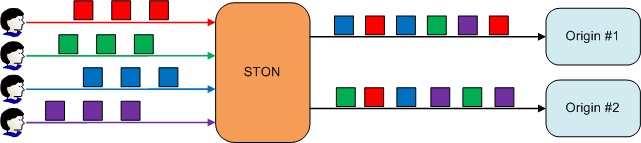
Requests will follow Origin Selection.
Fixed Origin Sessions¶
Each client socket will use a one-to-one bypass session with the origin server.
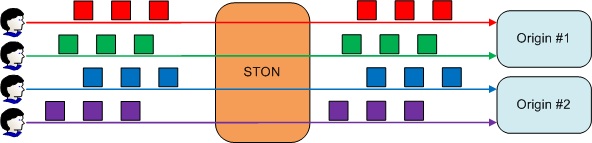
The client will have their own origin session.
Properties of GET/POST Bypass can be used to fix the origin session to the client.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><Options>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><Options>
<BypassPostRequest Private="OFF">...</BypassPostRequest>
<BypassGetRequest Private="OFF">...</BypassGetRequest>
PrivateONThe client session will have their own private session on the origin server. Requests will always be bypassed to the same server. Either the client or the origin server can terminate the session, at which point the session will be terminated on the other end as well.OFF (default)Private sessions are not used.
Just as origin servers hold on to the user’s login information within a session, it is helpful if the client handles requests within the same socket as well.
Note
If too many requests are bypassed with Private, there will be as many origin server connections as there are clients, creating an immense amount of load. Also, because origin sessions connected in this way are owned by the clients, it could endanger the server to malicious attacks.
Timeout¶
There are many cases when a bypass responds with results dynamically processed in the origin server. As such, there are many cases when processing speed is slower than static content. Setting a timeout specifically for bypasses is recommended to avoid the system prematurely assuming an error situation.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<BypassConnectTimeout>5</BypassConnectTimeout>
<BypassReceiveTimeout>300</BypassReceiveTimeout>
<BypassConnectTimeout> (default: 5 sec)If the bypass is unable to connect to the origin server within the set time, it will be considered a connection timeout.<BypassReceiveTimeout> (default: 5 sec)If there is no response from the origin server within the set time during a bypass, it will be considered a reception timeout.
Bypass Header¶
A bypass header configures whether or not to apply the bypass setting of Origin Request Default Header.
# server.xml - <Server><VHostDefault><OriginOptions>
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts><Vhost><OriginOptions>
<UserAgent Bypass="OFF">...</UserAgent>
<Host Bypass="ON"/>
<XFFClientIPOnly Bypass="ON">...</XFFClientIPOnly>
BypassPropertyONSpecifies the configured header.OFFSpecifies the relative headers sent by the clients.
Port Bypass¶
With a port bypass, the packets from a specific TCP port will all be bypassed to the origin server. This setting is exclusive to virtual hosts.
# vhosts.xml - <Vhosts>
<Vhost Name="www.example">
<PortBypass>443</PortBypass>
<PortBypass Dest=”1935”>1935</PortBypass>
</Vhost>
<PortBypass>Bypasses all packets from the designated port to the same port on the origin server. TheDestproperty configures the destination port on the origin server.
For example, bypassing port 443 will have an effect similar to creating a direct SSL connection with the origin server. Ports being bypassed can never have multiple redundant settings.
Note
Structurally, port bypasses take place in the TCP, a layer beneath HTTP. The reason for setting up a port bypass under a specific virtual host is that the virtual host is needed to collect statistics.